Gaming performance isn’t just about high frame rates; it’s also about how quickly your system responds to your inputs. NVIDIA’s Ultra-Low Latency Mode is designed to minimize input lag, ensuring your actions are reflected on-screen as quickly as possible. For competitive gamers and eSports enthusiasts, reducing input lag can mean the difference between winning and losing. This guide will take you through everything you need to know about this feature, how to enable it, and how to optimize your entire system for the lowest possible latency.
Understanding Input Lag and Its Impact on Gaming:
Input lag is the delay between pressing a key or clicking a mouse and seeing the corresponding action on the screen. This can be frustrating, particularly in fast-paced competitive games like first-person shooters or battle royale titles. High input lag results in delayed reactions, which can make a player feel sluggish and unresponsive compared to opponents with lower latency setups.
The key factors contributing to input lag include:
- Frame Buffering: Queuing frames before rendering increases latency.
- System Hardware: Low-end CPUs and GPUs struggle with real-time processing.
- Monitor Refresh Rate: Higher refresh rates reduce lag.
- Network Latency: Poor internet connections cause input delays.
NVIDIA’s Ultra-Low Latency Mode helps address one of the biggest contributors—frame buffering—by ensuring frames are sent to the GPU just in time for rendering, significantly reducing this delay.
How NVIDIA’s Ultra-Low Latency Mode Works?
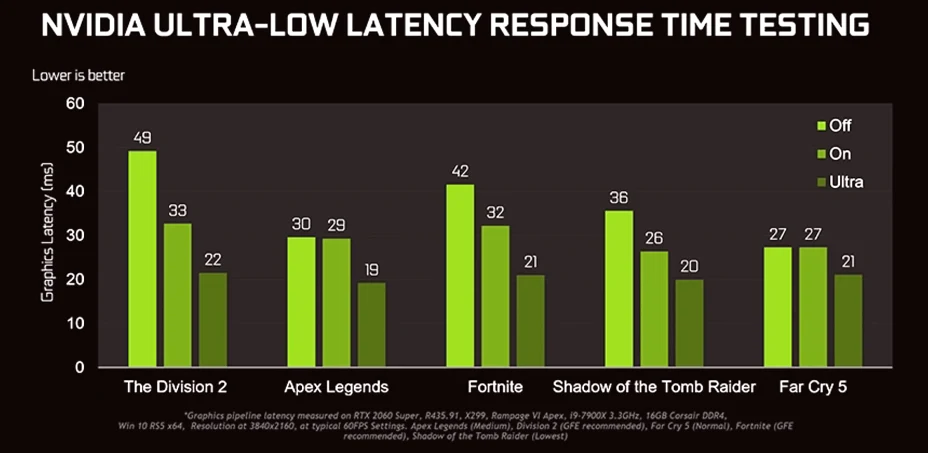
Traditionally, GPUs queue up frames to optimize performance and ensure smooth gameplay. However, queuing frames introduce latency because the CPU is working ahead of the GPU. This is where NVIDIA’s Ultra-Low Latency Mode changes the game. Instead of pre-rendering multiple frames, this mode allows the GPU to render frames just in time for display, reducing the overall lag and making gameplay feel significantly more responsive.
Key Benefits:
- Reduces input lag by up to 33%.
- Improves responsiveness in fast-paced games.
- Works with DirectX 9 and DirectX 11 games.
- Does not require additional hardware.
How to Enable NVIDIA Ultra-Low Latency Mode?
Follow these steps to enable Ultra-Low Latency Mode:
- Right-click on your desktop and open NVIDIA Control Panel.
- Navigate to Manage 3D settings in the left panel.
- Scroll down to Low Latency Mode under the Global Settings or Program Settings tab.
- Set it to Ultra and click Apply.
Common Issues and Potential Drawbacks:
While Ultra-Low Latency Mode is an excellent feature, it does have some potential downsides:
- Increased CPU Load: Since this mode requires real-time frame rendering, it may increase CPU usage, especially on older processors.
- Not Effective for All Games: Some modern games already have optimized frame queuing, making this setting unnecessary.
- Potential FPS Drops: On systems with lower-end CPUs or when running CPU-intensive games, enabling this mode may cause slight frame rate drops or occasional stutters.
If you experience performance issues after enabling this feature, consider tweaking other settings or testing it on a game-by-game basis rather than applying it globally.
Additional Tips to Reduce Input Lag:
- Use a High Refresh Rate Monitor: A 144Hz or 240Hz gaming monitor reduces motion blur and improves screen responsiveness.
- Enable NVIDIA Reflex (If Available): Reflex works directly with game engines to reduce system latency even further.
- Adjust Graphics Settings: Lower shadow quality, reflections, and anti-aliasing to reduce rendering times.
- Optimize Your Network Connection: Use a wired Ethernet connection and lower background network traffic.
- Close Background Processes: Close unnecessary applications using Task Manager to free up CPU resources.
FAQs:
No, this feature primarily benefits DirectX 9 and DirectX 11 games. Newer games optimized for low latency may not see significant improvements.
No, this setting is designed to reduce input lag, not increase FPS. However, it can make your gaming experience feel smoother.
On some lower-end CPUs, enabling this feature may introduce performance issues such as FPS drops or micro-stutters. If this happens, try disabling it and using alternative methods to optimize your gaming experience.
Test responsiveness in fast-paced games by performing quick movements and observing input response. Additionally, tools like NVIDIA’s FrameView can help measure latency improvements.
No, Ultra-Low Latency Mode is exclusive to NVIDIA GPUs. AMD offers a similar feature called Anti-Lag, which functions similarly but is not identical.
Aside from Ultra-Low Latency Mode, you can also:
1. Use a gaming mouse and keyboard with low latency.
2. Set Windows Power Plan to High Performance.
3. Reduce screen resolution for faster frame rendering.
4. Keep GPU and motherboard firmware updated.
Yes, but Reflex is generally more effective and should be prioritized in supported games.
Conclusion:
NVIDIA’s Ultra-Low Latency Mode is a powerful tool for reducing input lag and improving responsiveness. While it doesn’t boost FPS, it significantly enhances the fluidity of gameplay by reducing the delay between input and action.
By enabling this feature, optimizing game settings, and using complementary tools like NVIDIA Reflex, you can achieve an incredibly responsive gaming experience. However, always test and tweak your setup to ensure it works optimally for your hardware and gaming preferences.
For gamers looking for the fastest reaction times, Ultra-Low Latency Mode is a must-try feature that could make all the difference in clutch moments.